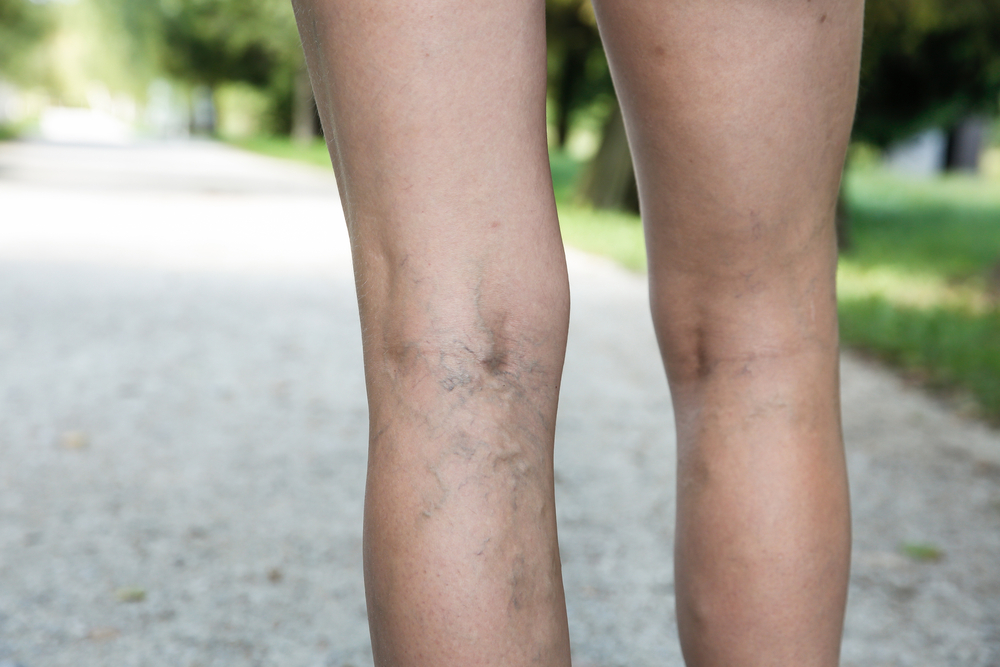
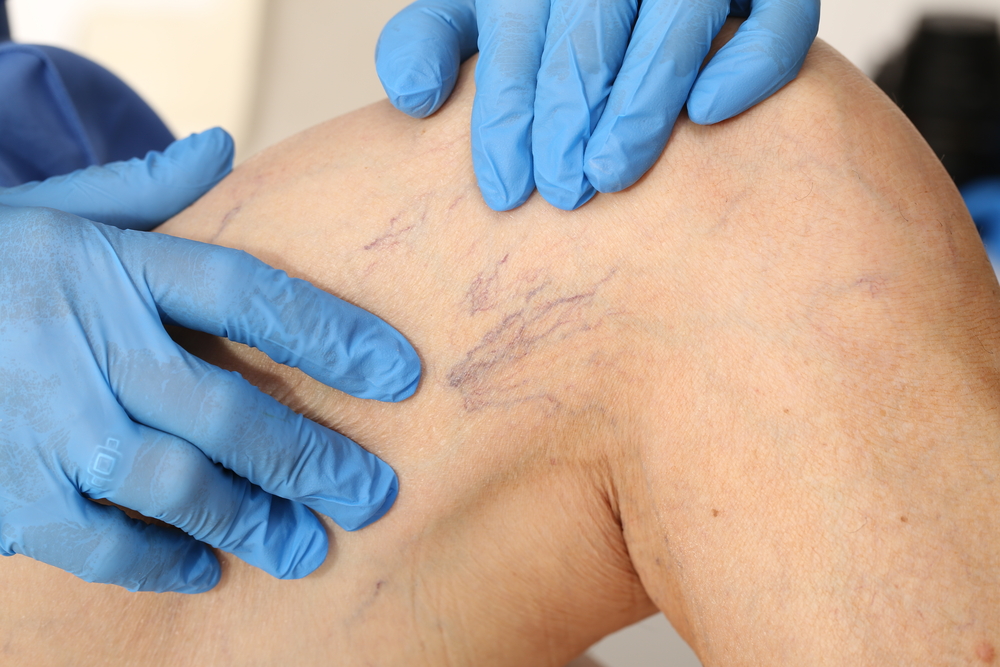
Varicose Veins
Varicose veins are enlarged, swollen, twisted, dilated veins. They are often dark purple or blue and usually develop on the inside of the legs and the back of the calves. Any vein can become varicose, but the legs are most commonly affected. Older people are more likely to develop varicose veins due to changes in the veins that are common with age. Some pregnant women can develop varicose veins. Obesity and prolonged sitting or standing can also cause varicose veins. Symptoms include skin color changes, itching, rashes, as well as numbness, aching, burning and heaviness in the legs. Varicose veins get worse over time.
Spider Veins
Spider veins are a mild variation of varicose veins. They typically appear as clusters of red, blue and purple lines, and are visible on the surface of the skin. Spider veins look like thin lines, and are at times connected together like tree branches or spider webs. Spider veins are more of a cosmetic issue. They normally develop on the thighs, feet and ankles, and also appear on the chin and around the nose. No one knows what exactly causes spider veins. Treatment focuses on eliminating them due to their unattractive appearance.
Chronic Venous Insufficiency
Veins feature tiny valves that open as blood flows toward the heart, and close to prevent blood from flowing backward. Chronic venous insufficiency (CVI) occurs when the valves do not work properly, enabling blood to flow backward. Valves can become damaged due to aging, or prolonged sitting or standing. Blood pools or collects in the valves. Symptoms of CVI include leg ulcers, skin color changes, swelling in the foot or leg, and pressure, itching, heaviness or tightness in the calves or legs.
Vein Treatment
The VeinGogh Ohmic Thermolysis System™
The VeinGogh Ohmic Thermolysis System™ generates a tiny, regulated, high frequency current delivered to the vessel via a hair-thin probe. A “microburst” of energy selectively heats the vein, coagulating the blood and collapsing the vessel wall, which is quickly absorbed into the body. All this is accomplished without affecting the outer layers of the skin resulting in a quick return to normal daily activities.
The VeinGogh Ohmic Thermolysis System™ is a superior solution for the treatment of fine telangiectasia, spider veins and small angiomas. It yields fast, immediate, consistent, repeatable results, with little or no discomfort. It is useful in treating a wide range of fine vessels, vascular abnormalities and skin tags, anywhere on the body. It clears even recalcitrant vessels left by other therapies. It can treat any skin type, usually only a single treatment is required and you can resume normal activities right after treatment.

Sclerotherapy
Sclerotherapy is a widely used non-surgical procedure. Often used as an alternative to surgery, sclerotherapy can reduce or eliminate spider and varicose veins in one to six treatments, depending upon the extent of the problem and patient compliance following the procedure. It has been estimated that as many as 50%-80% of treated veins may be eliminated with each session of sclerotherapy.
During the procedure, a salt solution is injected into the targeted vein using an ultra-fine needle. Patients may experience mild discomfort and cramping for a couple of minutes as the solution is being injected. The procedure usually takes between 15-30 minutes.
Patients can resume normal daily activities immediately following the procedure. Walking is actually encouraged.
Support hosiery will need to be worn to compress the treated vessels. While Tylenol can be taken if needed, it is important to avoid taking aspirin, ibuprofen or other anti-inflammatory medications for at least 48 hours following treatment. Patients should also avoid taking hot baths, applying hot compresses or being in direct sunlight for at least 48 hours after treatment.
There are certain side effects that patients may experience following sclerotherapy, including itching and raised, red areas around the injection site, which should subside within a few days. Bruising could also occur lasting several days or weeks. While allergic reactions are rarely serious, if you experience sudden swelling in the leg, the formation of ulcers around the injection site or inflammation within five inches of the groin, please contact your doctor immediately.


Endovenous Laser Treatment
Endovenous laser treatment (EVLT) is a quick, minimally invasive treatment. It takes about an hour and results in very little to no discomfort. During the procedure, a small optic fiber is inserted through a needle into the affected vein using an ultrasound. As the laser is activated, the optic fiber is removed from the damaged vein, while it heats and closes the vein; which causes blood to reroute to nearby healthy veins. Over time, the body absorbs the closed vein. EVLT cannot be used to treat veins that are too small. Only a light sedative or local anesthesia is needed for treatment. Patients must wear compression stockings for a week or more after treatment to reduce swelling and promote healing. Doctors typically encourage patients to walk immediately after EVLT and resume normal activities.
Other Conditions
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) occurs when a blood clot develops in one or more of the deep veins in the body, typically the legs. DVT can cause pain, but often no symptoms occur. DVT is a serious condition. A blood clot can break loose, travel through the blood stream and lodge in the lungs; blocking blood flow. This is known as pulmonary embolism. Pulmonary embolism can be fatal.
Symptoms of DVT include:
- Swelling
- Pain
- Skin color changes (turning pale, red or blue)
Endovenous Laser Treatment
- Sitting for long periods of time. When your legs are still for long periods, the calf muscles don’t contract. This usually helps blood to circulate. If the calf muscles aren’t moving, blood clots can form.
- Surgery or injury. A vein injury or surgery can slow down blood flow; increasing the risk of bloo
- Long periods of bed rest, such as during a hospital stay or due to paralysis. The calf muscles don’t contract when sitting still for long periods of time, which can cause blood clots to develop.
Treatment
Treatment of DVT focuses on preventing the blood clot from getting larger, and from breaking loose. The goal of treatment is also to keep DVT from occurring again. Your doctor may prescribe blood thinners to prevent blood clots from getting larger and reduce the likelihood that more clots will form. If you can’t tolerate blood thinners, a filter may be inserted into a large vein in the abdomen (the vena cava). Filters prevent blood clots from breaking loose. Your doctor may also recommend you wear compression stockings for at least a year. Compression stockings prevent swelling, and reduce the likelihood that your blood will pool and clot.
If you think you may have DVT, please consult your doctor.

